
Apply non-sterile gloves and goggles or face shield according to agency protocols. Figure 4.3 Hemovac drain Figure 4.4 Jackson-Pratt drainĬhecklist 39 outlines the steps to take when emptying a closed wound drainage system.įor example: drainage measurement container, non-sterile gloves, waterproof pad, and alcohol swabģ. The drainage site is covered with a sterile dressing and should be checked periodically to ensure the drain is functioning effectively and that no leaking is occurring.
REMOVE ADVANCED CARE SYSTEM SKIN
Drains are usually sutured to the skin to prevent accidental removal. A Jackson-Pratt (JP) drain (see Figure 4.4) is usually used for smaller amounts of drainage (25 to 50 ml). A Hemovac drain (see Figure 4.3) can hold up to 500 ml of drainage. Drainage may vary depending on location and type of surgery. The drainage is collected in a closed sterile collection system/reservoir (Hemovac or Jackson-Pratt) or an open system that deposits the drainage on a sterile dressing.
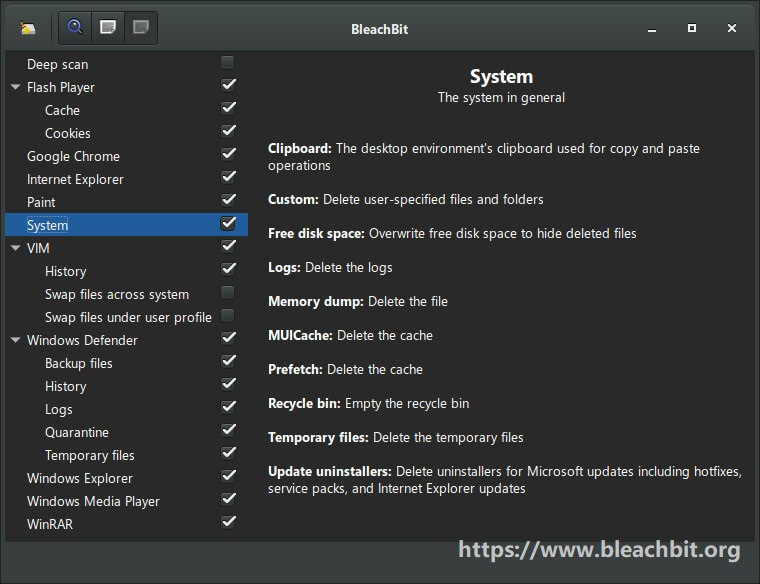
Closed systems must be emptied and measured at least once every shift and cleaned using sterile technique according to agency protocol.ĭrainage tubes consist of silastic tubes with perforations to allow fluid to drain from the surgical wound site, or separate puncture holes close to the surgical area. A closed system uses a vacuum system to withdraw fluids and collects the drainage into a reservoir.

The number of drains depends on the extent and type of surgery. A drain may be superficial to the skin or deep in an organ, duct, or a cavity such as a hematoma. 4.7 Drain Management and Removal Drain Managementĭrains systems are a common feature of post-operative surgical management and are used to remove drainage from a wound bed to prevent infection and the delay of wound healing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
